|
JeVois
1.23
JeVois Smart Embedded Machine Vision Toolkit
|
|
|
JeVois
1.23
JeVois Smart Embedded Machine Vision Toolkit
|
|
The hardware serial port (UART port) on your JeVois smart camera is TTL-level (not RS-232 levels) and supports both 3.3V and 5V logic.
The logic voltage to use is supplied by the connected microcontroller to the smart camera (RED wire, IOREF voltage). This voltage should be provided by your micro-controller and should be the voltage at which your RX and TX signals operate). Arduino boards provide the IOREF pin for this purpose. IOREF is an input to JeVois. Thus, a 5V Arduino will output 5V to IOREF, and will use 5V levels for RX and TX. In contrast, a 3.3V Arduino will output 3.3V to IOREF and will use 3.3V levels for RX and TX.
To connect to an Arduino board, you would typically do as follows ( JeVois-A33 is shown, pinout is the same for JeVois-Pro):
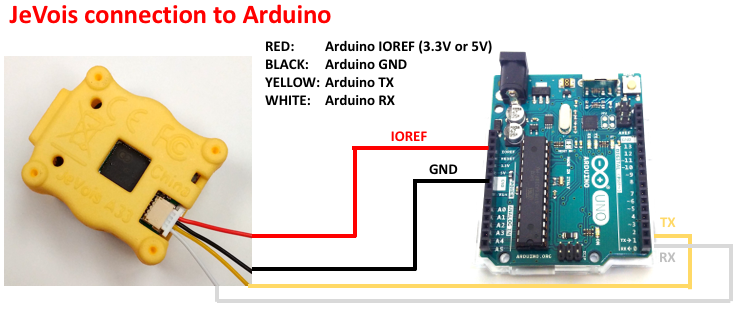
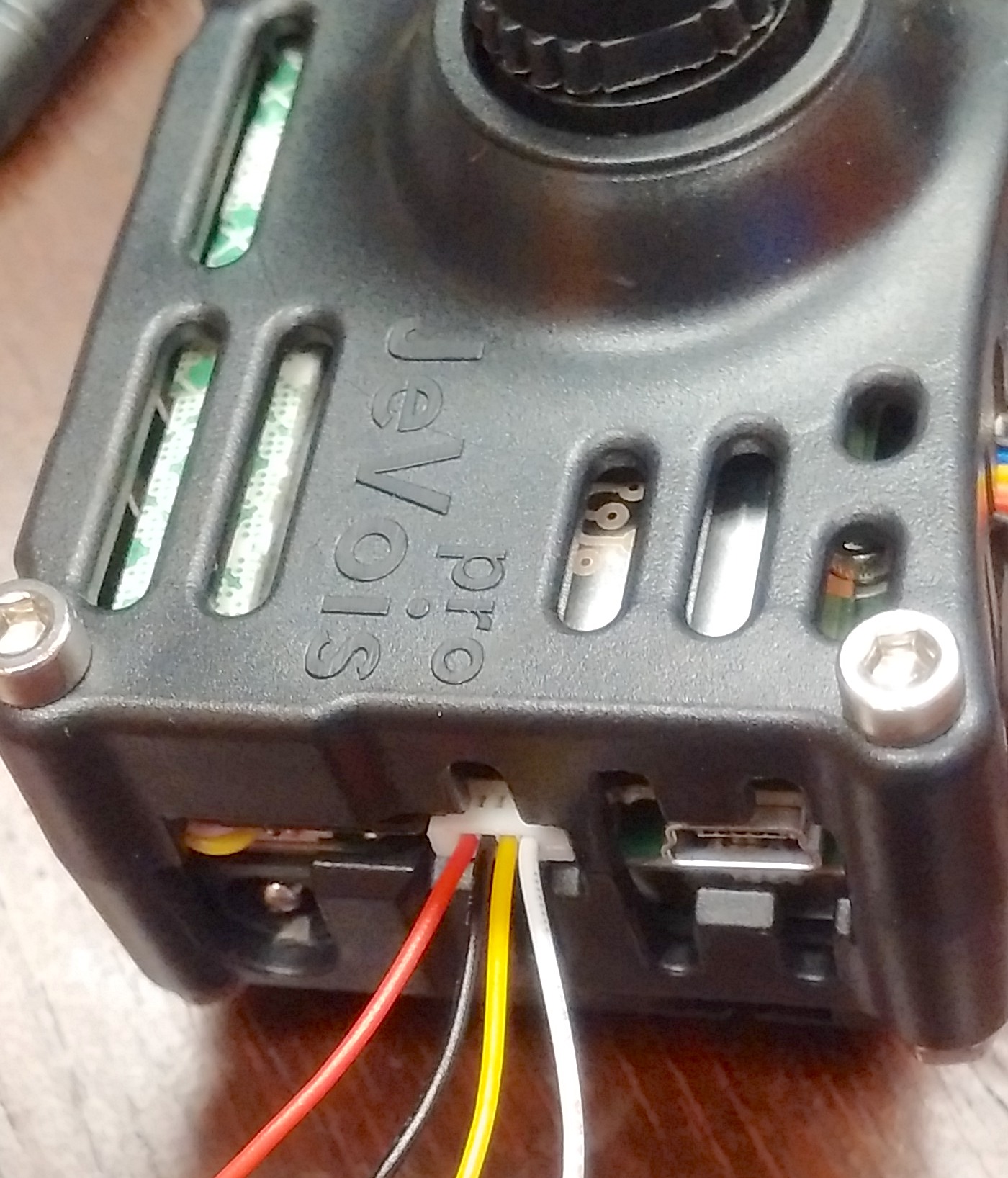
Note the orientation of the connector and the order of the colored wires, for JeVois-A33 above and JeVois-Pro below:

You can customize the settings of the serial port to match what your microcontroller can support, by editing the file JEVOIS:/config/params.cfg on your microSD card (source in ~/jevois/Config/params.cfg). The following options are supported (see The jevois-daemon executable for more configurations options supported at startup, and see jevois::Serial for full documentation of the serial interface):
For example, to reduce the serial rate to 9600 bauds when piping the serial data to a Bluetooth BLE transmitter, params.cfg should contain:
serialdev=/dev/ttyS0 serial:baudrate=9600 serial:linestyle=LF
We have successfully used an Adafruit Feather 32u4 Bluefruit LE to transmit JeVois serial data over bluetooth. Using this, you can control JeVois from a tablet running a bluetooth serial app (such as the BlueFruit app).
We connected its serial pins to the serial port of JeVois, and wrote a trivial piece of code that would just forward serial data between the serial pins and the BLE module of the Feather. It worked well at 9600 bauds but choked at 115200 bauds. Looks like serial transmission over BLE is limited to 9600 bauds. Have a look in JEVOIS:/config/params.cfg for config options we used when transmitting serial data over Bluetooth. Other serial-to-BLE modules are available and should work fine as well, but we have not yet tested. The main drawback with the Feather 32u4 Bluefruit LE is its price ($30).