|
JeVois Tutorials
1.23
JeVois Smart Embedded Machine Vision Tutorials
|
|
|
JeVois Tutorials
1.23
JeVois Smart Embedded Machine Vision Tutorials
|
|
This tutorial develops a simplistic module that leverages optical character recognition (OCR) as supported by JeVois through OpenCV and the Tesseract library, which is available through the OpenCV Text module (including from Python).
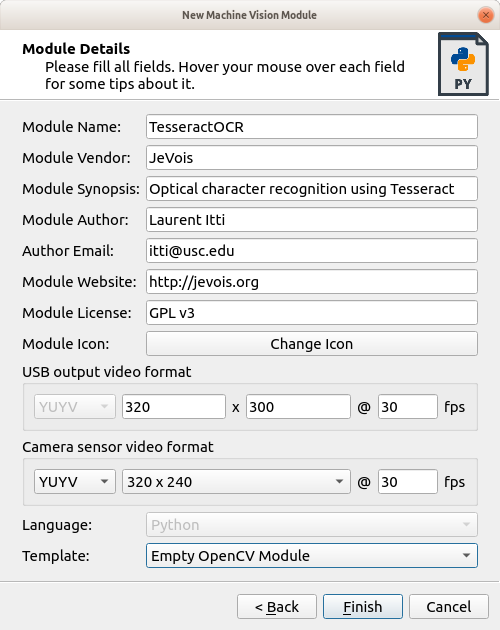
CTRL-N).Fill in the details as shown below:
So, here we have decided to have a 60-pixel-tall area below the input image, where we will write the decoded text.
A bit of web search for OpenCV and Tesseract gets us to https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/d7/ddc/classcv_1_1text_1_1OCRTesseract.html which we will use to get our code going.
Basically, we need to create an OCR object (which we should do only once, hence we will do that in the constructor of our module), and then we will call run() on it with an image and a confidence level as inputs, getting decoded text (if any) as a result. We can finally send that text to serial and also write it into our output display.
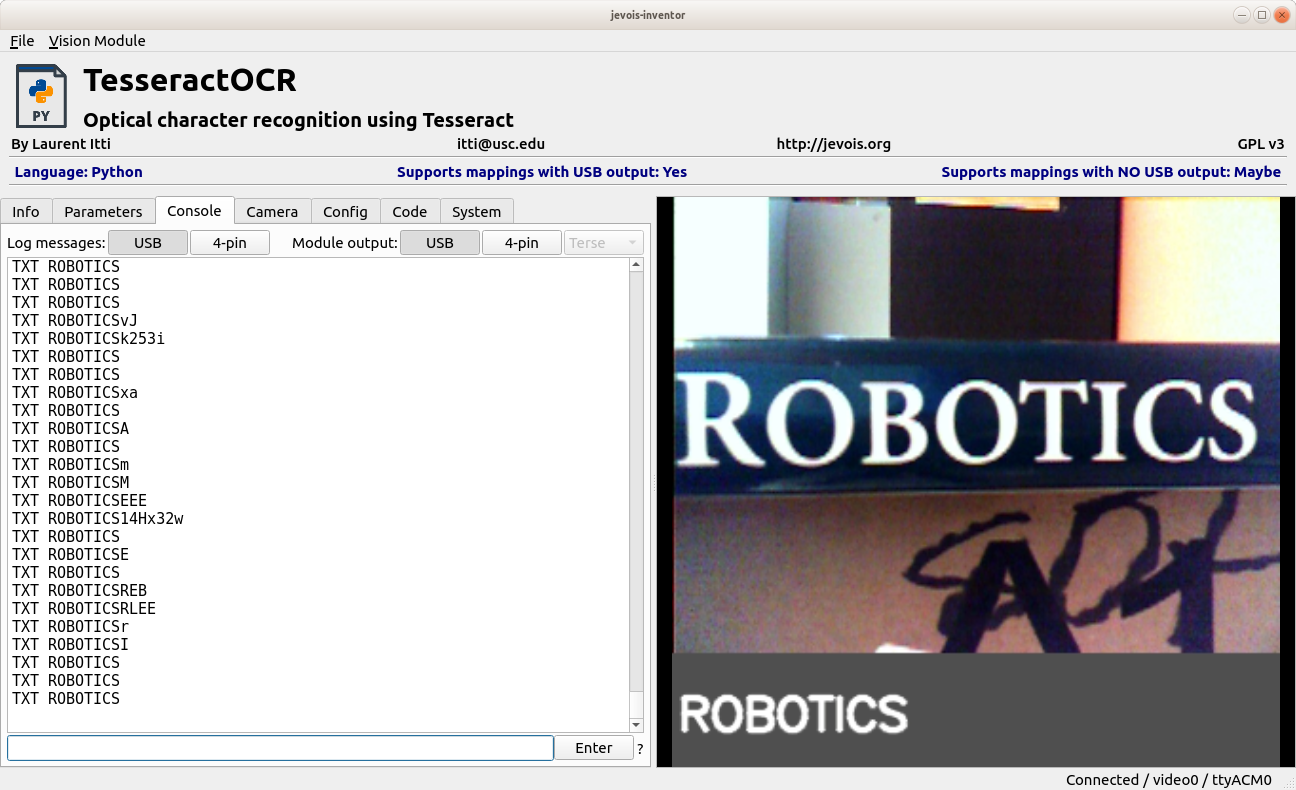
First, let's get the OCR part done, just sending decoded text to serial port. Then we will worry about making the composite display later.
Enable Module output to USB in the Console tab of the Inventor and... This is working!
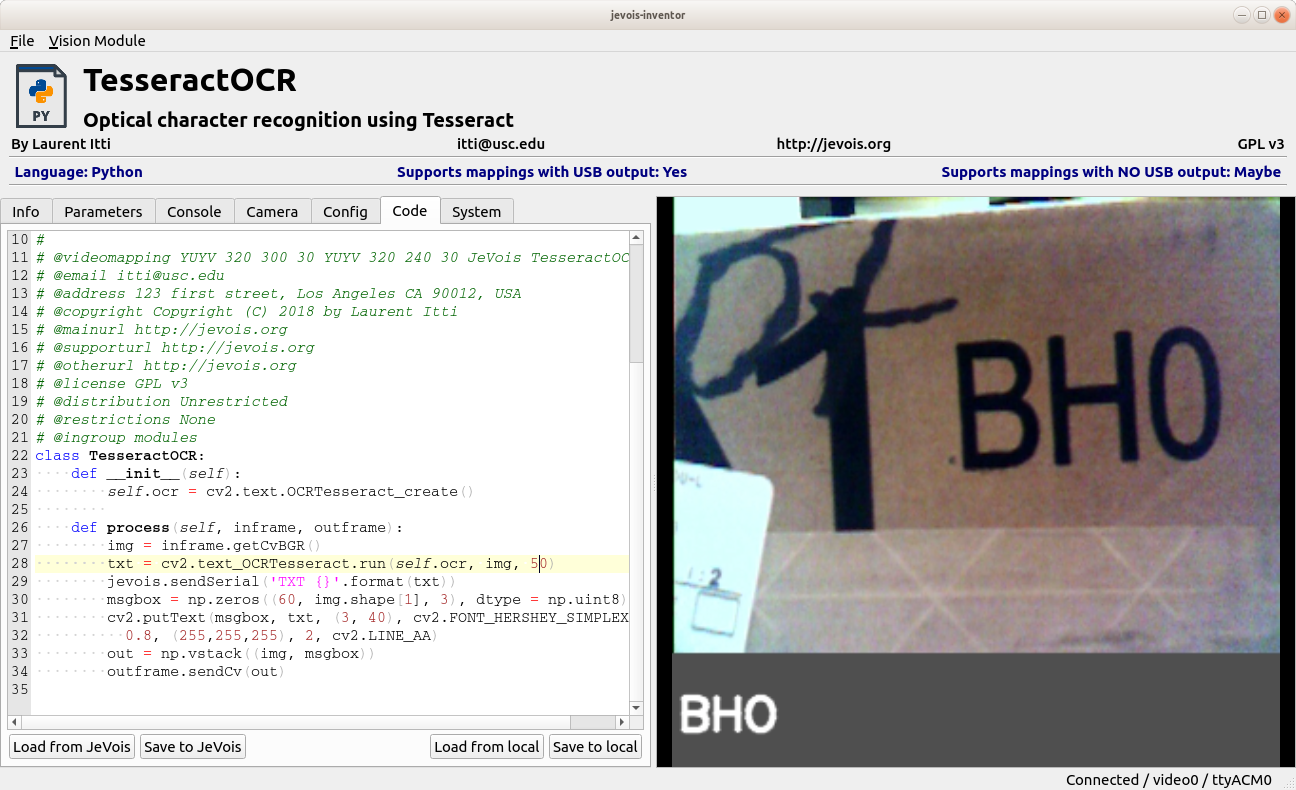
We now just add a few lines of code to render the decoded text into a small message area below the video frame, and to stack both images up, as in Creating composite output video frames
Here we go!
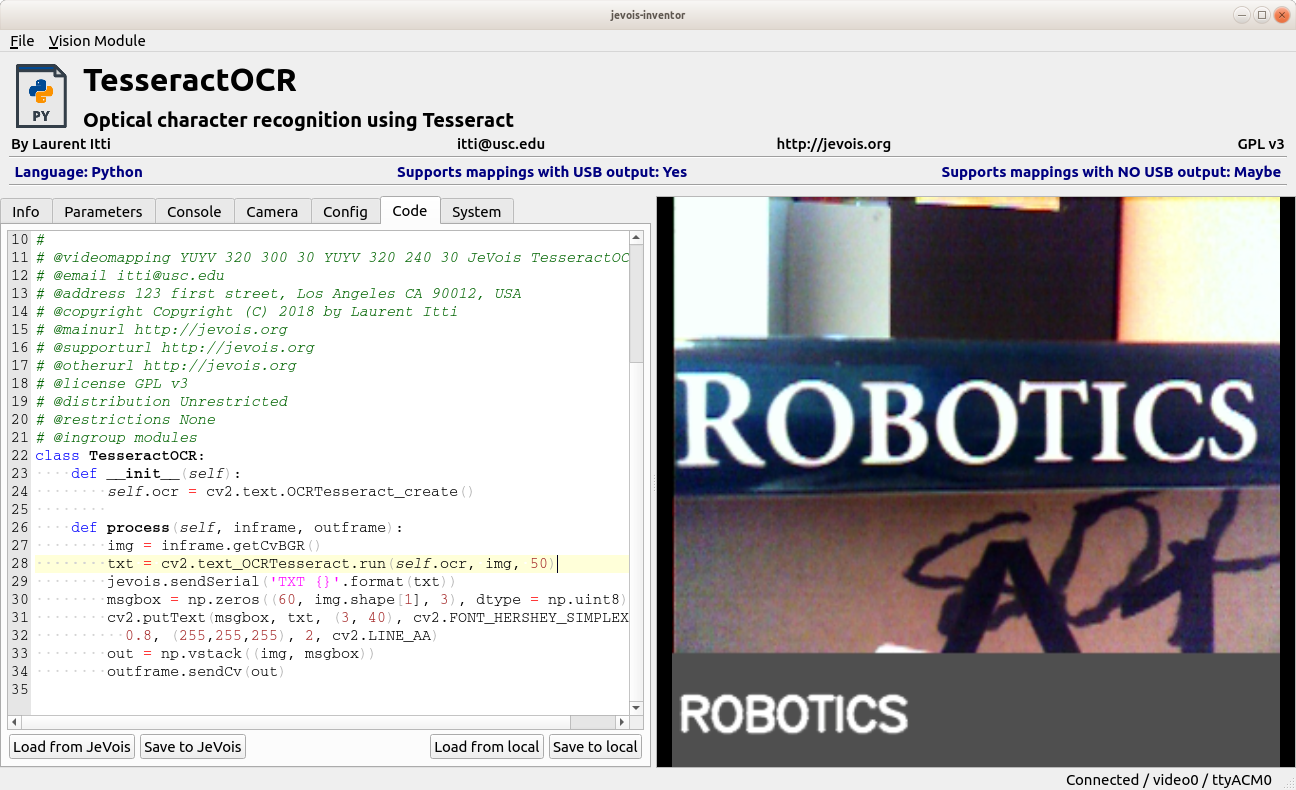
As mentioned above, better results will be obtained by implementing a pipeline that first extracts candidate boxes around each word, then sends each box to OCR (which can be parallelized over multiple boxes).
See for example https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib/blob/master/modules/text/samples/end_to_end_recognition.cpp (but it is written in C++, so some work will be needed to translate to python if desired).
 1.9.8
1.9.8