|
| By Laurent Itti | itti@usc.edu | http://jevois.org | GPL v3 |
| |||
| Video Mapping: YUYV 320 252 30.0 YUYV 320 240 30.0 JeVois ObjectDetect |
Module Documentation
This module finds objects by matching keypoint descriptors between the current image and a set of training images. Here we use SURF keypoints and descriptors as provided by OpenCV.
The algorithm consists of 4 phases:
- detect keypoint locations, typically corners or other distinctive texture elements or markings;
- compute keypoint descriptors, which are summary representations of the image neighborhood around each keypoint;
- match descriptors from current image to descriptors previously extracted from training images;
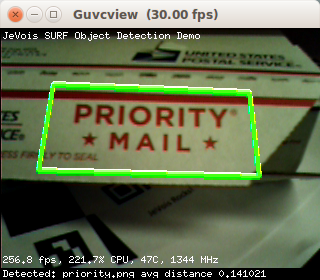
- if enough matches are found between the current image and a given training image, and they are of good enough quality, compute the homography (geometric transformation) between keypoint locations in that training image and locations of the matching keypoints in the current image. If it is well conditioned (i.e., a 3D viewpoint change could well explain how the keypoints moved between the training and current images), declare that a match was found, and draw a green rectangle around the detected object.
The algorithm comes by default with one training image, for the Priority Mail logo of the U.S. Postal Service. Search for "USPS priority mail" on the web and point JeVois to a picture of the logo on your screen to recognize it. See the screenshots of this module for examples of how that logo looks.
Offline training
Simply add images of the objects you want to detect in JEVOIS:/modules/JeVois/ObjectDetect/images/ on your JeVois microSD card. Those will be processed when the module starts. The names of recognized objects returned by this module are simply the file names of the pictures you have added in that directory. No additional training procedure is needed. Beware that the more images you add, the slower the algorithm will run, and the higher your chances of confusions among several of your objects.
With JeVois v1.1 or later, you do not need to eject the microSD from JeVois, and you can instead add images live by exporting the microSD inside JeVois using the usbsd command. See MicroSD card organization and files (last section) for details. When you are done adding new images or deleting unwanted ones, properly eject the virtual USB flash drive, and JeVois will restart and load the new training data.
Live training
With JeVois v1.2 and later you can train this algorithm live by telling JeVois to capture and save an image of an object, which can be used later to identify this object again.
First, enable display of a training window using:
setpar showwin true
You should now see a gray rectangle. You can adjust the window size and aspect ratio using the win parameter. By default, the algorithm will train new objects that occupy half the width and height of the camera image.
Point your JeVois camera to a clean view of an object you want to learn (if possible, with a blank, featureless background, as this algorithm does not attempt to segment objects and would otherwise also learn features of the background as part of the object). Make sure the objects fits inside the gray rectangle and fills as much of it as possible. You should adjust the distance between the object and the camera, and the grey rectangle, to roughly match the distance at which you want to detect that object in the future. Then issue the command:
save somename
over a serial connection to JeVois, where somename is the name you want to give to this object. This will grab the current camera image, crop it using the gray rectangle, and save the crop as a new training image somename.png for immediate use. The algorithm will immediately re-train on all objects, including the new one. You should see the object being detected shortly after you send your save command. Note that we save the image as grayscale since this algorithm does not use color anyway.
You can see the list of current images by using command:
list
Finally, you can delete an image using command:
del somename
where somename is the object name without extension, and a .png extension will be added. The image will immediately be deleted and that object will not be recognized anymore.
For more information, see JeVois tutorial Live training of the Object Detection module and the associated video:
Serial Messages
This module can send standardized serial messages as described in Standardized serial messages formatting. One message is issued on every video frame for the best detected object (highest score).
- Serial message type: 2D
id: filename of the recognized objectx,y: standardized 2D coordinates of the object centerw,h, or vertices: Standardized bounding box around the objectextra: none (empty string)
See Standardized serial messages formatting for more on standardized serial messages, and Helper functions to convert coordinates from camera resolution to standardized for more info on standardized coordinates.
Programmer notes
This algorithm is quite slow. So, here, we alternate between computing keypoints and descriptors on one frame (or more, depending on how slow that gets), and doing the matching on the next frame. This module also provides an example of letting some computation happen even after we exit the process() function. Here, we keep detecting keypoints and computing descriptors even outside process(). The itsKPfut future is our handle to that thread, and we also use it to alternate between detection and matching on alternating frames.
| Custom module commands |
|---|
| list - show current list of training images |
| save somename - grab current frame and save as new training image somename.png |
| del somename - delete training image somename.png |
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ObjectDetect) win | floatpair | Width and height (in percent of image size, with valid percentages between 10.0 and 100.0) of the window used to interactively save objects | floatpair(50.0F, 50.0F) | - |
| (ObjectDetect) showwin | bool | Show the interactive image capture window when true | false | - |
| (ObjectMatcher) hessian | double | Hessian threshold | 800.0 | - |
| (ObjectMatcher) traindir | std::string | Directory where training images are | images | - |
| (ObjectMatcher) goodpts | jevois::Range<size_t> | Number range of good matches considered | jevois::Range<size_t>(15, 100) | - |
| (ObjectMatcher) distthresh | double | Maximum distance for a match to be considered good | 0.2 | - |
| Detailed docs: | ObjectDetect |
|---|---|
| Copyright: | Copyright (C) 2016 by Laurent Itti, iLab and the University of Southern California |
| License: | GPL v3 |
| Distribution: | Unrestricted |
| Restrictions: | None |
| Support URL: | http://jevois.org/doc |
| Other URL: | http://iLab.usc.edu |
| Address: | University of Southern California, HNB-07A, 3641 Watt Way, Los Angeles, CA 90089-2520, USA |